English page
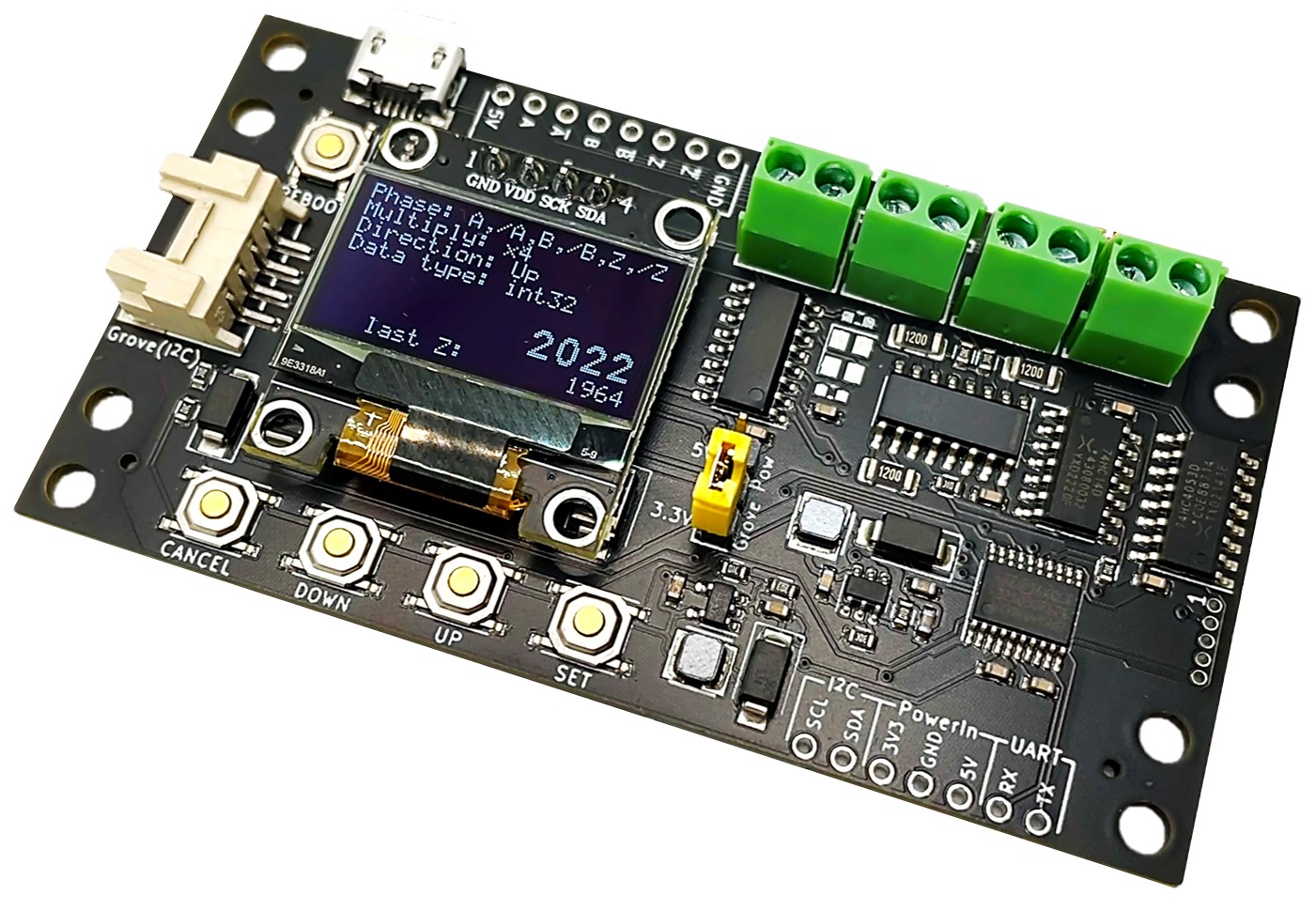
インクリメンタル出力のエンコーダのパルスをカウントし表示・出力するモジュールです。
位相は2相(A・B)と3相(A・B・Z)、出力方式はオープンコレクタ出力、電圧出力、ラインドライバ出力のエンコーダに対応しています。
通信インターフェイスはUSB、Grove(I2C)に対応しています。
電源はUSBバスパワー、Grove(3.3V)、外部入力(5V or 3.3V)に対応しています。
DINレール取付けとネジ取付けの両方に対応しています。
部品は全て実装済みのため、はんだ付けは不要です。
3D CADデータもダウンロードいただけます。
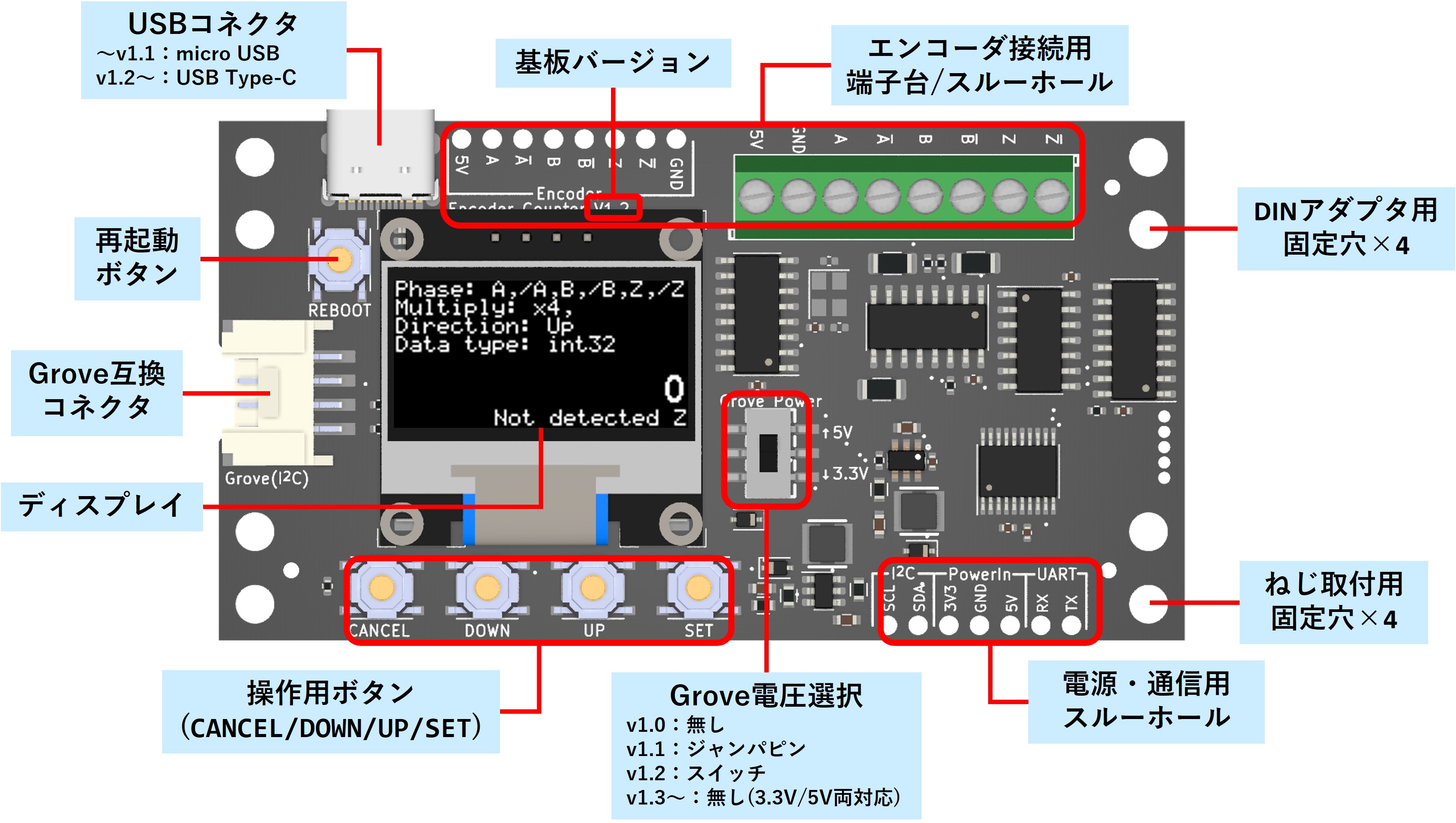
各部の名称
内容物
製品本体×1
※エンコーダや各種ケーブル、取付用アダプタは含まれていません。別途ご用意いただく必要があります。
販売
※販売ページに表示されている在庫数のほかにも、追加の在庫を保有している場合がございます。大量注文や在庫に関する問い合わせはこちらまでご連絡ください。
使い方
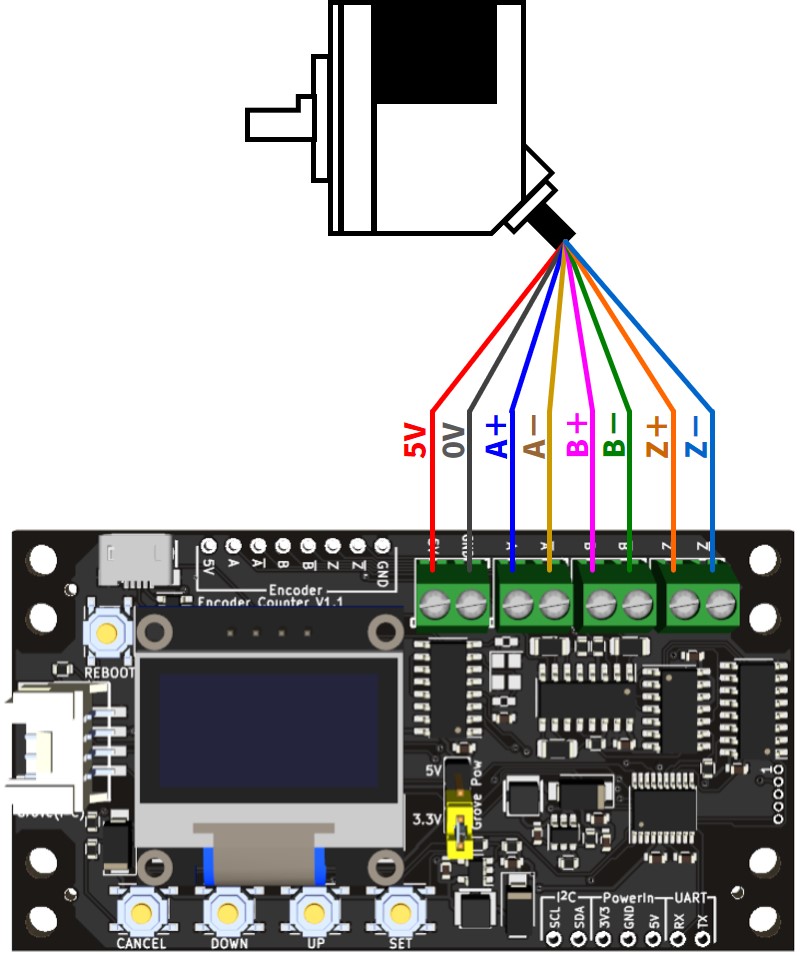
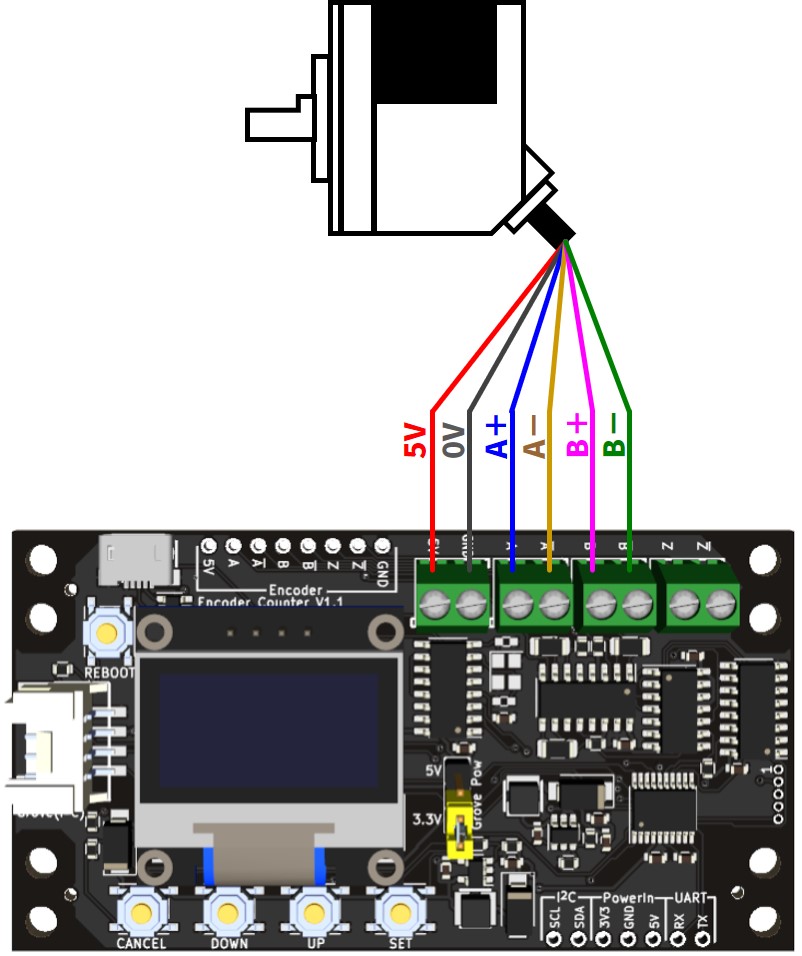
エンコーダを接続する
ラインドライバ出力の場合(DC5V)
3相
2相
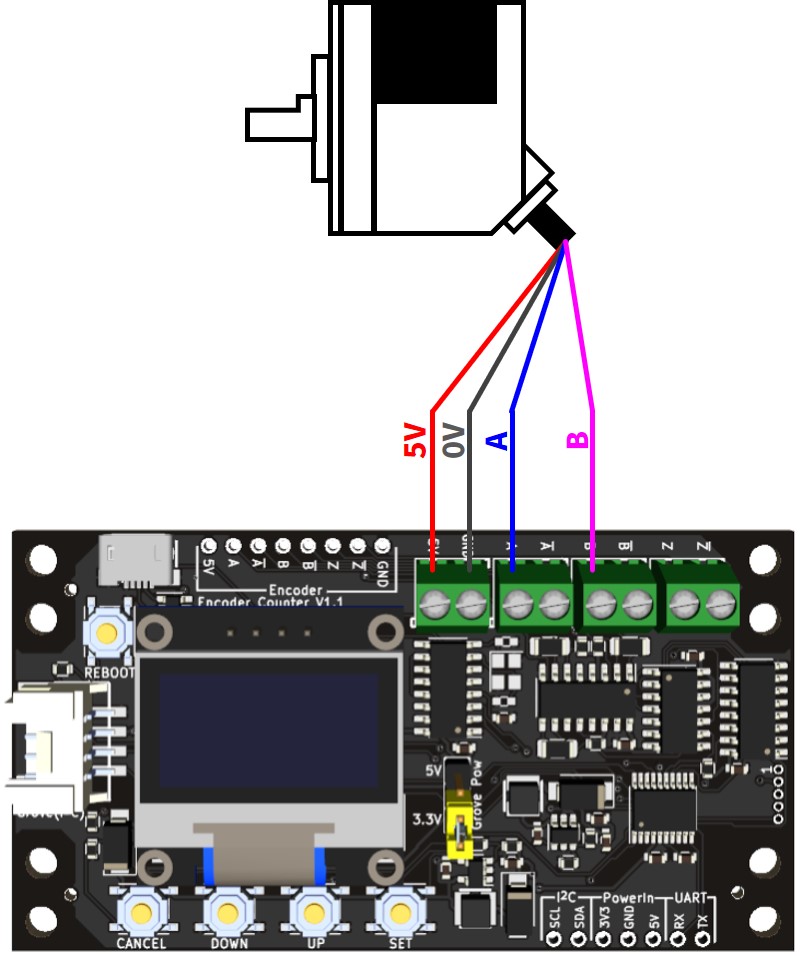
電圧出力/NPNオープンコレクタ出力の場合(DC5V) 1
3相
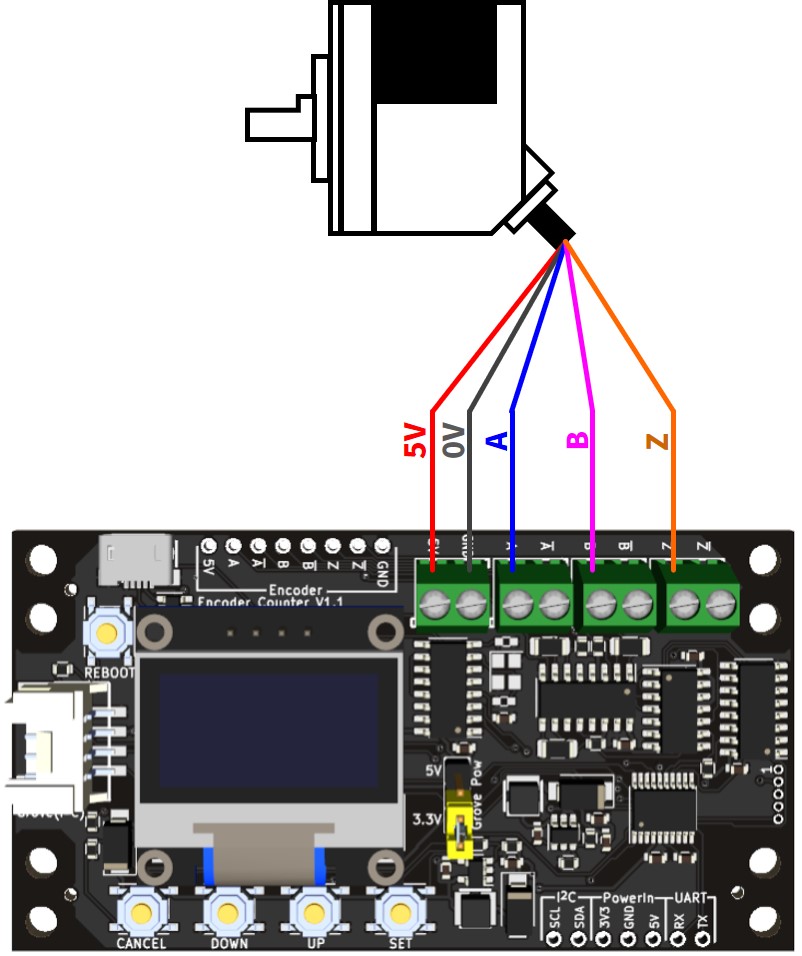
2相
機械式エンコーダの場合
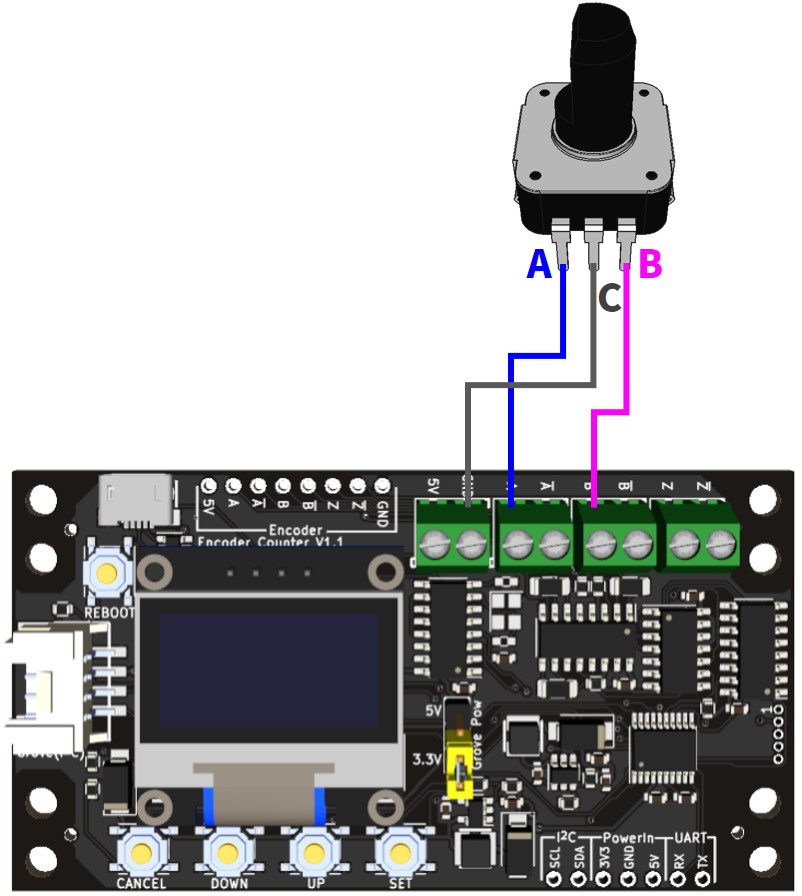
※エンコーダ接続用の端子台とスルーホールは基板内で電気的に接続されているため、エンコーダを端子台の代わりにスルーホールに接続することも可能です。
電源に接続する
以下のいずれかの方法で電源を供給して下さい。- USB給電(5V)
- Grove互換コネクタ(3.3V 2)
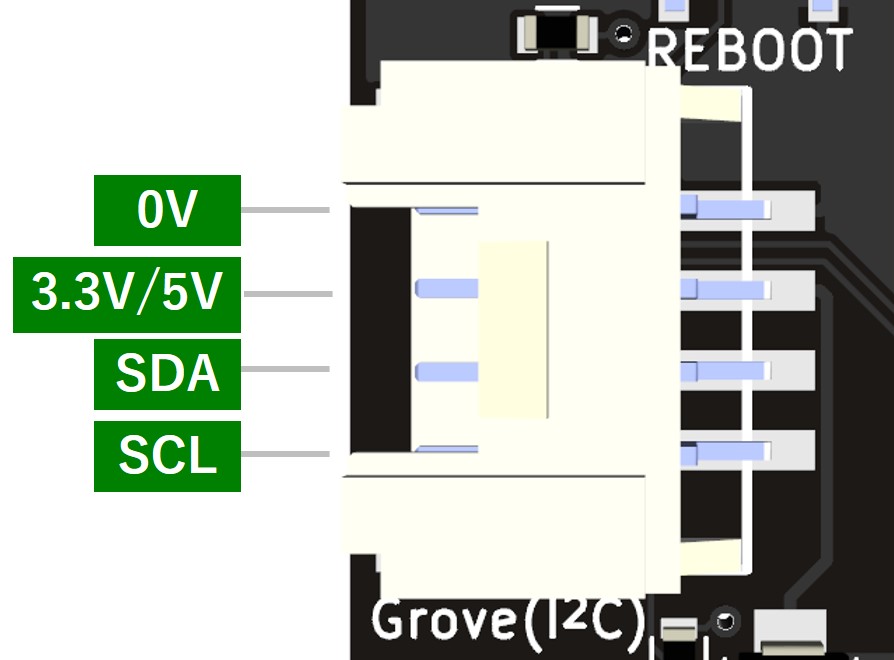
ピン配置図 - 電源用スルーホール(5V)
- 電源用スルーホール(3.3V)
※5V系のUSBと電源用スルーホール(5V)、および3.3V系のGroveコネクタと電源用スルーホール(3.3V)は基板内で電気的に接続されているため、同電圧系統に複数の電源を接続しないでください。
※5V系と3.3V系の双方に電源を接続しても構いません。たとえば、USB(5V)とGrove(3.3V)の双方から電源を供給しても問題ありません。
※エンコーダの消費電力を賄える電源を接続してください。設定する
基板上のボタンもしくはI2Cコマンドでエンコーダと通信の設定を行ってください。
通信仕様
I2C
レジスタマップシリアル通信(USB、UART)
- 出力フォーマット
- Z相有効化時:
<カウント値>:<Z相の最終検出時のカウント値>:<Z相検出後:1、Z相未検出:0>\n(例:12345:7890:1\n) - Z相無効化時:
<カウント値>(例:12345\n)
- Z相有効化時:
- コマンド
以下の1文字(改行コードなし)を製品に送ると実行されます。c:カウント値取得。上記出力フォーマットの文字列を送信する。USB Tx Modeが有効な場合は無効。r:カウントリセット。カウント値を初期値、Z相を未検出状態にする。
- 出力フォーマット
仕様
- 対応エンコーダ
- 位相:2相(A・B)、3相(A・B・Z)
- 出力方式:5Vラインドライバ出力(AM26C31相当)、5V電圧出力、オープンコレクタ出力
- エンコーダの電源電圧:5 V (※電源を本製品から供給する場合)
- エンコーダの最大消費電流:250 mA以下(※電源を本製品から供給する場合)
- カウンタ
- 入力チャンネル数:1
- 最大入力周波数:5 MHz (※出力方式や配線環境によります)
- カウンタ更新周期:1 ms
- カウント範囲:32 bit(符号付き/符号なしを選択可)
- 通信インターフェース:USB、Grove互換コネクタ(I2C)、スルーホール(UART/I2C)
- 給電方式:USBバスパワー、Grove互換コネクタ (3.3V 2)、スルーホール(5V/3.3V)
- シリアル通信(USB・UART)
- ボーレート:921600 bps
- データビット:8 bit
- パリティ:なし
- ストップビット:1 bit
- UARTの信号電圧:3.3 V
- I2C
- 最大通信速度:400 kbps
- 信号電圧:3.3V
- 外形寸法:W80 x D43 x H12 mm
- その他
- USBシリアル変換IC:WCH CH340 3
画面遷移図
設定項目の説明
Reset countカウントリセット。カウント値を初期値、Z相を未検出状態にする。Phase位相と出力方式の設定- *
A,/A,B,/B,Z,/Z出力相:3相、出力方式:ラインドライバ出力 A,B,Z出力相:3相、出力方式:電圧出力/オープンコレクタ出力A,/A,B,/B出力相:2相、出力方式:ラインドライバ出力A,B出力相:2相、出力方式:電圧出力/オープンコレクタ出力
- *
Multiply逓倍設定- *
x44逓倍 x2_A2逓倍(A相エッジでカウント)x2_B2逓倍(B相エッジでカウント)
- *
Cnt directionカウント方向- *
Up Down
- *
Data typeカウント値のデータ型- *
int32符号付き32bit整数 (-2147483648 ~ 2147483647、初期値:0) uint32符号なし32bit整数 (0 ~ 4294967295、初期値:2147483648)
- *
USB Tx ModeUSB・UARTでのカウント値の取得方法の設定- *
Auto自動モード。カウント値を1ms周期で自動的に送信する Manual手動モード。カウント値はコマンド(c)が入力されると送信する。
- *
I2C AddressI2Cデバイスアドレス- *
0x11 0x120x130x14
- *
Save and reboot変更したパラメータを保存し、製品を再起動するReset all settings全ての項目を工場出荷時の設定に戻し、製品を再起動するAbout製品情報とファームウェアのバージョンを表示する
* 工場出荷時の設定
取付方法
DINレール取付け
DINレールアダプタ(Phoenix Contact社 1201578)を画像のようにネジ止めしてください。
※DINレールアダプタ・ねじ等は付属しません。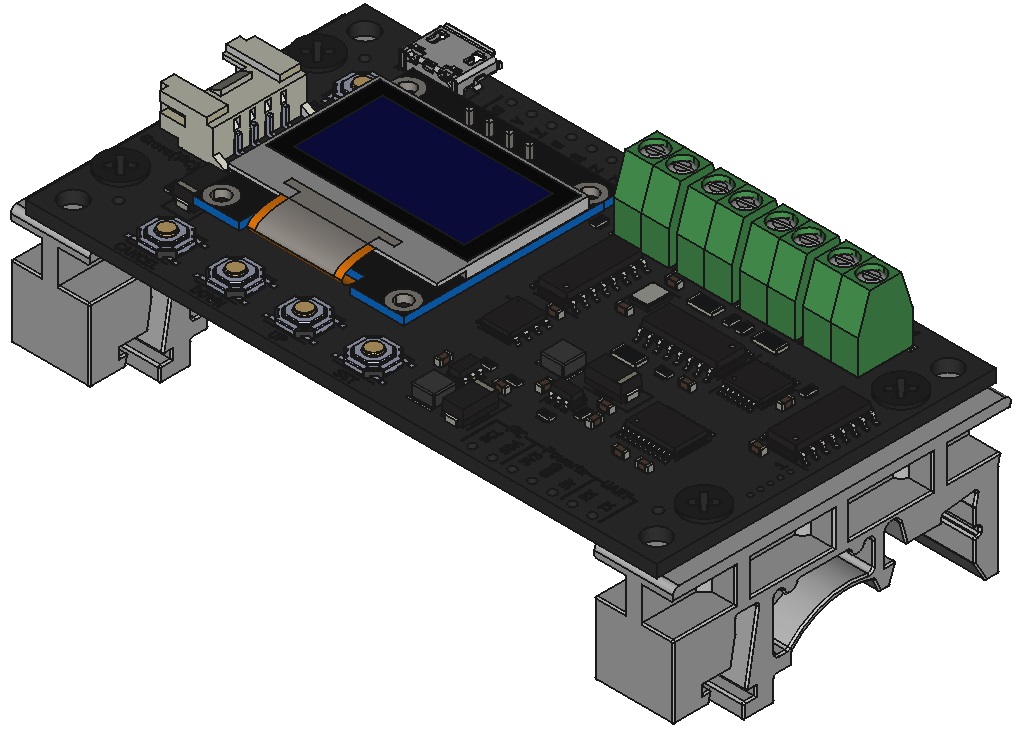
ねじ取付け
スペーサ等を用いて所望の板等に固定してください。
※スペーサ・ねじ等は付属しません。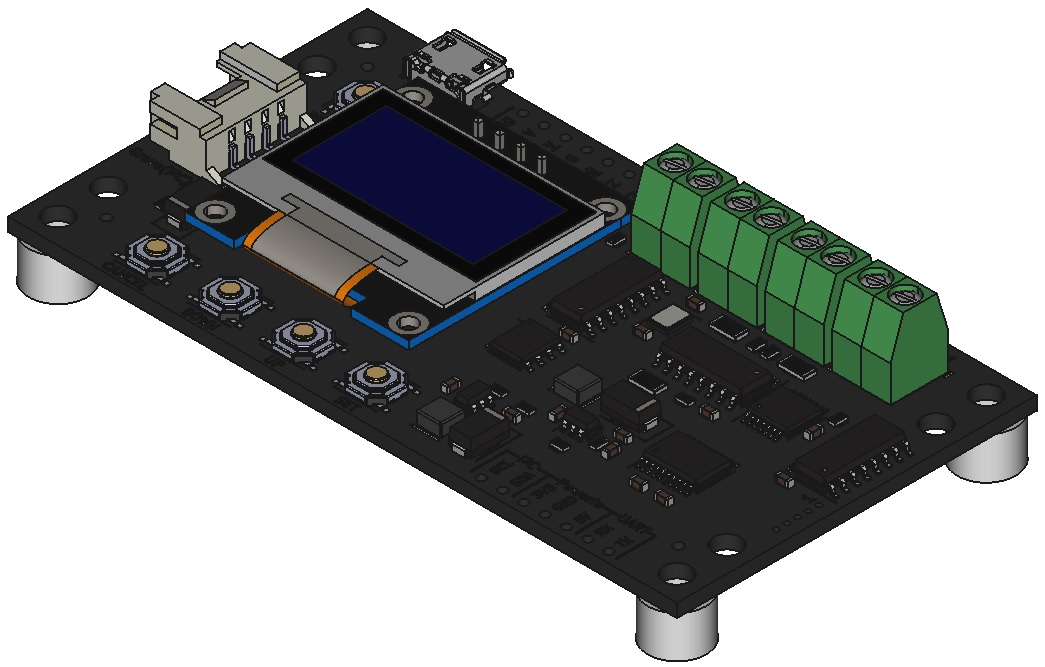
ファームウェアのアップデート
詳細を見る
必要なもの
- 製品本体
- USBケーブル
- PC
必要なソフトウェア
本製品に搭載しているSTMicroelectronics社のマイコンへの書込み用ソフト"STM32CubeProg"が必要です。 下記のサイトからソフトウェアをダウンロードしインストールしてください。
https://www.st.com/ja/development-tools/stm32cubeprog.html
※本ソフトウェアをダウンロードするためにはmySTへの登録(無料)が必要です。
ファームウェアの書き換え手順
資料
回路図
- v1.0: schematic-v1_0.pdf
- v1.1: schematic-v1_1.pdf
- v1.2: schematic-v1_2.pdf
- v1.3: schematic-v1_3.pdf
外形寸法
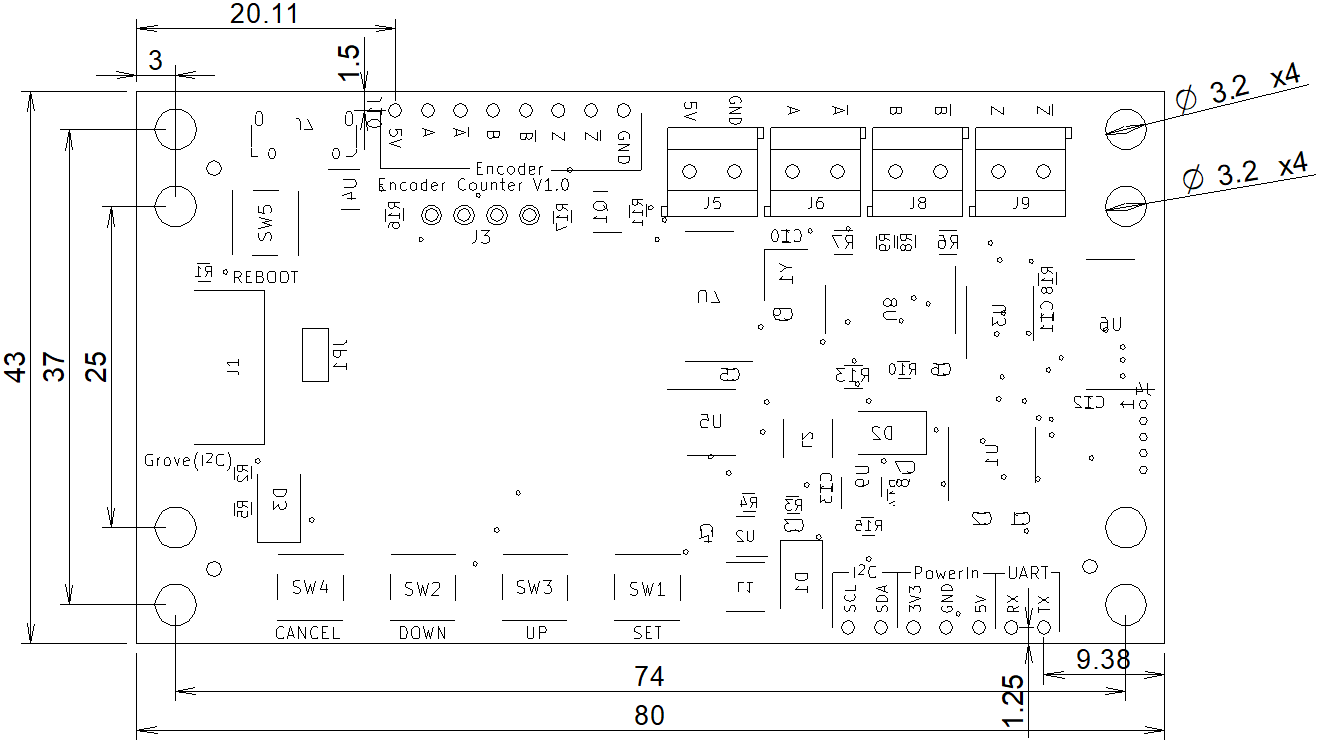 DXFファイル:dimensional_dxf.zip
DXFファイル:dimensional_dxf.zip3D CADデータ
STEPファイル:encoder_counter_step.zip
プログラム例
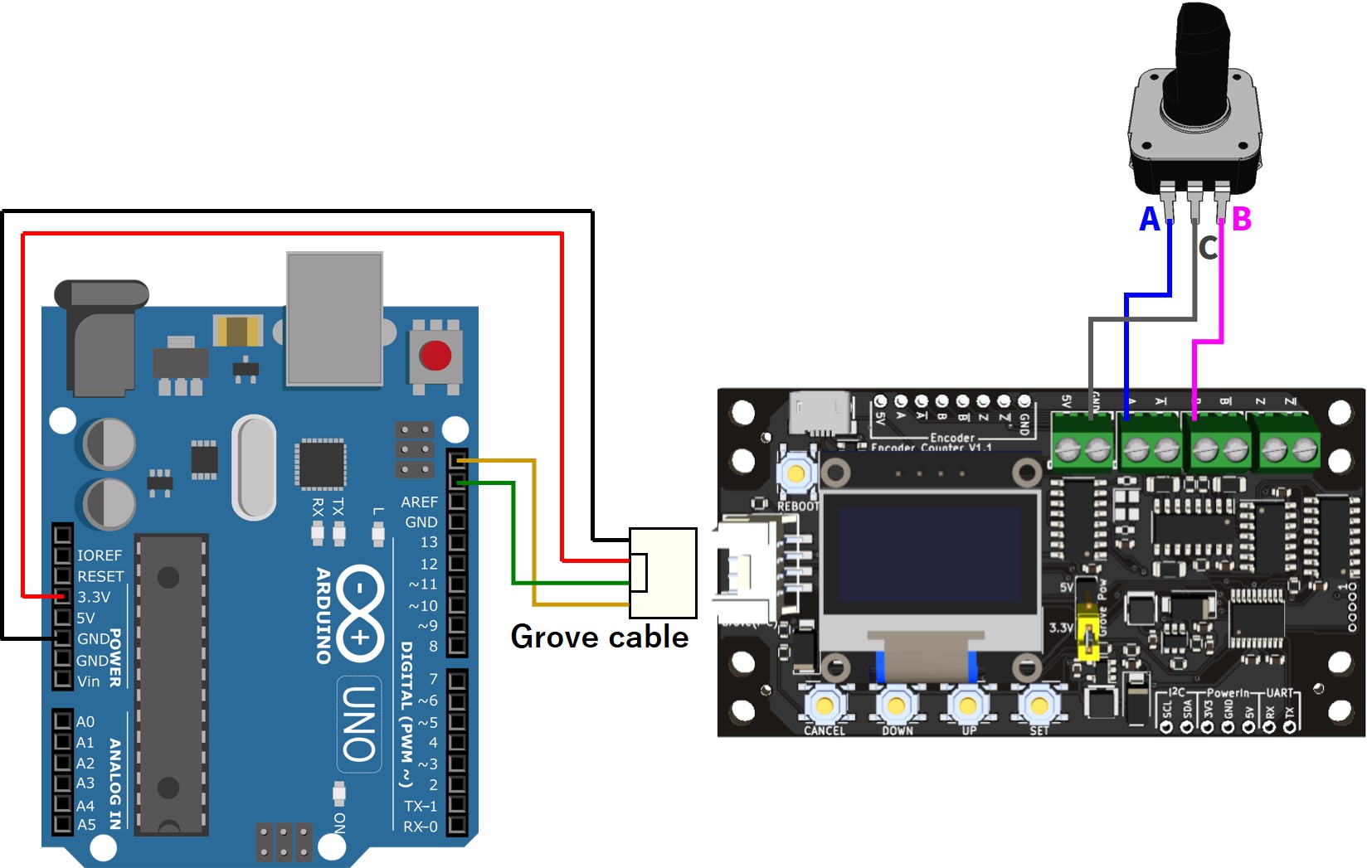
ArduinoのI2Cを用いたカウント値取得のプログラム例
配線図・サンプルコードを見る
#include <stdint.h>
#include <Wire.h>
#define I2C_SLAVE_DEV_ADDR 0x11
// Register address
#define ESTATUS_REG_ADDR 0x01
#define CRST_REG_ADDR 0x02
#define CVAL_REG_ADDR 0x03 // 0x03 - 0x06
#define RCVAL_REG_ADDR 0x07 // 0x07 - 0x0A
#define ECONF_REG_ADDR 0x0B
#define CCONF_REG_ADDR 0x0C
#define VMAJOR_REG_ADDR 0x0D
#define VMINOR_REG_ADDR 0x0E
#define VPATCH_REG_ADDR 0x0F
#define SYSRBT_REG_ADDR 0x10
#define I2CADDR_REG_ADDR 0x11
#define INIT_REG_ADDR 0x12
typedef union _32bit_u
{
uint8_t uint8_data[4];
uint32_t uint32_data;
int32_t int32_data;
} _32bit_u;
void setup() {
// Communication function init
Serial.begin(115200);
while (!Serial);
// I2C init
Wire.begin();
Wire.setClock(400000);
byte error;
// Set encoder config
// ECONF: Data type=int32, Count dir=Up, Multiply=x2_A, Phase=A,B
uint8_t econf = 0x07;
Wire.beginTransmission(I2C_SLAVE_DEV_ADDR);
Wire.write(ECONF_REG_ADDR);
Wire.write(econf);
error = Wire.endTransmission();
if (error){
Serial.print("error=");Serial.println(error);
}
delay(4000); // Wait until the config is written and the device reboots
}
void loop() {
delay(100);
// Read encoder count
_32bit_u count;
Wire.beginTransmission(I2C_SLAVE_DEV_ADDR);
Wire.write(CVAL_REG_ADDR);
Wire.endTransmission(false);
Wire.requestFrom(I2C_SLAVE_DEV_ADDR, 4);
for(int i = 0; i < 4; i++) {
count.uint8_data[i] = Wire.read();
}
Serial.print("count = ");Serial.println(count.int32_data);
}
STM32(Nucleo)のI2Cを用いたカウント値取得のプログラム例
配線図・サンプルコードを見る
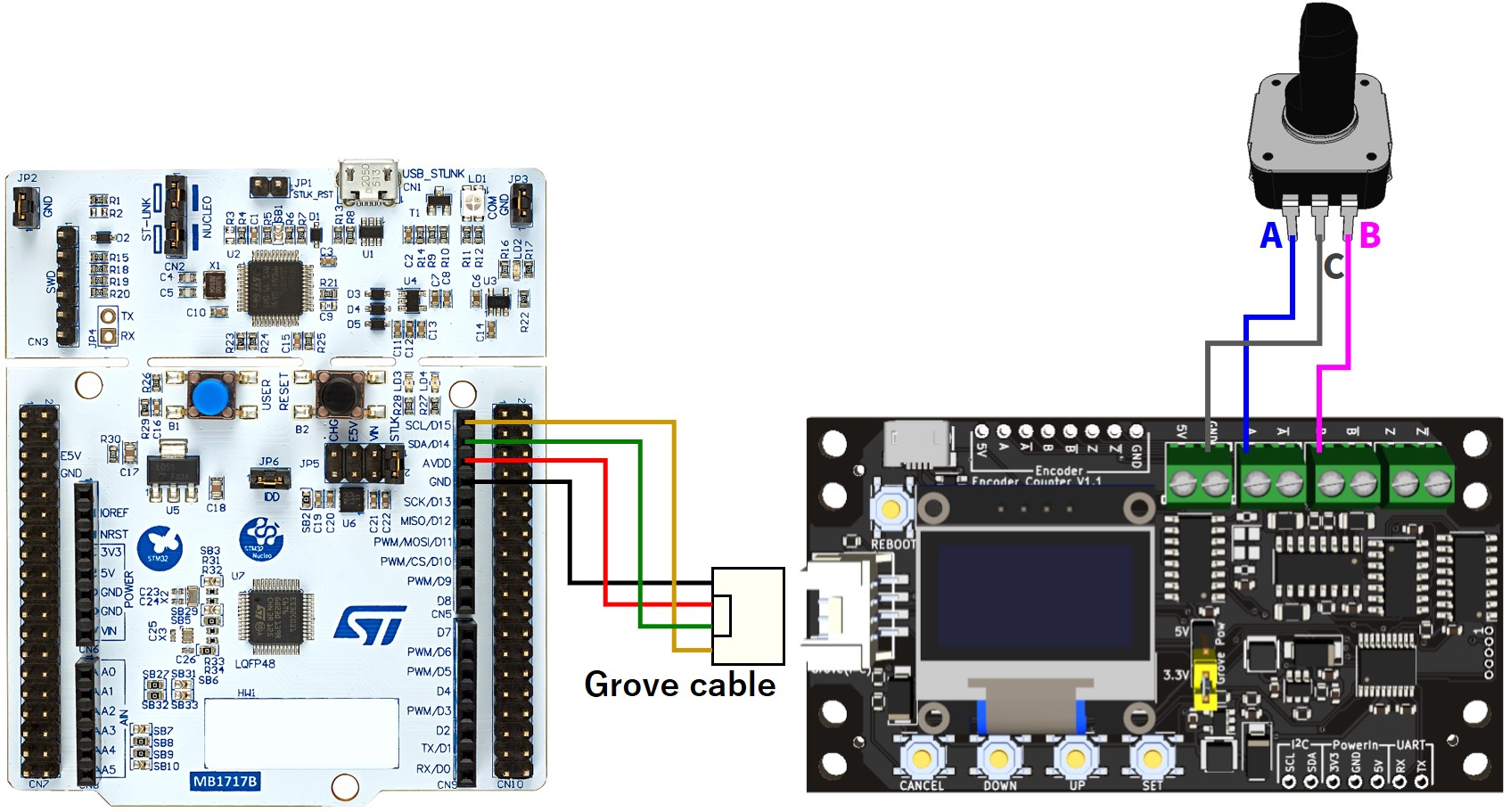
サンプルコード(主要部分のみ抽出)
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdbool.h>
#include <stdint.h>
#include "i2c.h"
#include "usart.h"
typedef union _32bit_u
{
uint32_t uint32_data;
int32_t int32_data;
uint8_t uint8_data[4];
} _32bit_u;
#define I2C_MASTER_INSTANCE I2C1
#define I2C_MASTER_HANDLE_PTR &hi2c1
#define I2C_SLAVE_DEV_ADDR 0x11
// Register address
#define ESTATUS_REG_ADDR 0x01
#define CRST_REG_ADDR 0x02
#define CVAL_REG_ADDR 0x03 // 0x03 - 0x06
#define RCVAL_REG_ADDR 0x07 // 0x07 - 0x0A
#define ECONF_REG_ADDR 0x0B
#define CCONF_REG_ADDR 0x0C
#define VMAJOR_REG_ADDR 0x0D
#define VMINOR_REG_ADDR 0x0E
#define VPATCH_REG_ADDR 0x0F
#define SYSRBT_REG_ADDR 0x10
#define I2CADDR_REG_ADDR 0x11
#define INIT_REG_ADDR 0x12
int main(void)
{
// ----- Omit initialization process ----- //
HAL_StatusTypeDef status;
// Set encoder config
// ECONF: Data type=int32, Count dir=Up, Multiply=x2_A, Phase=A,B
uint8_t econf = 0x07;
status = HAL_I2C_Mem_Write(I2C_MASTER_HANDLE_PTR, I2C_SLAVE_DEV_ADDR << 1, ECONF_REG_ADDR, I2C_MEMADD_SIZE_8BIT, &econf, 1, 1000);
if(status != HAL_OK)
printf("Error: %d\n", status);
HAL_Delay(4000); // Wait until the config is written and the device reboots
while (1) {
HAL_Delay(100);
// Read encoder count
_32bit_u count;
status = HAL_I2C_Mem_Read(I2C_MASTER_HANDLE_PTR, I2C_SLAVE_DEV_ADDR << 1, CVAL_REG_ADDR, I2C_MEMADD_SIZE_8BIT, &count.uint8_data[0], 4, 1000);
if(status == HAL_OK)
printf("count = %d\n", count.int32_data);
else
printf("Error: %d\n", status);
}
}
Raspberry Pi PicoのI2Cを用いたカウント値取得のプログラム例(MicroPython)
配線図・サンプルコードを見る
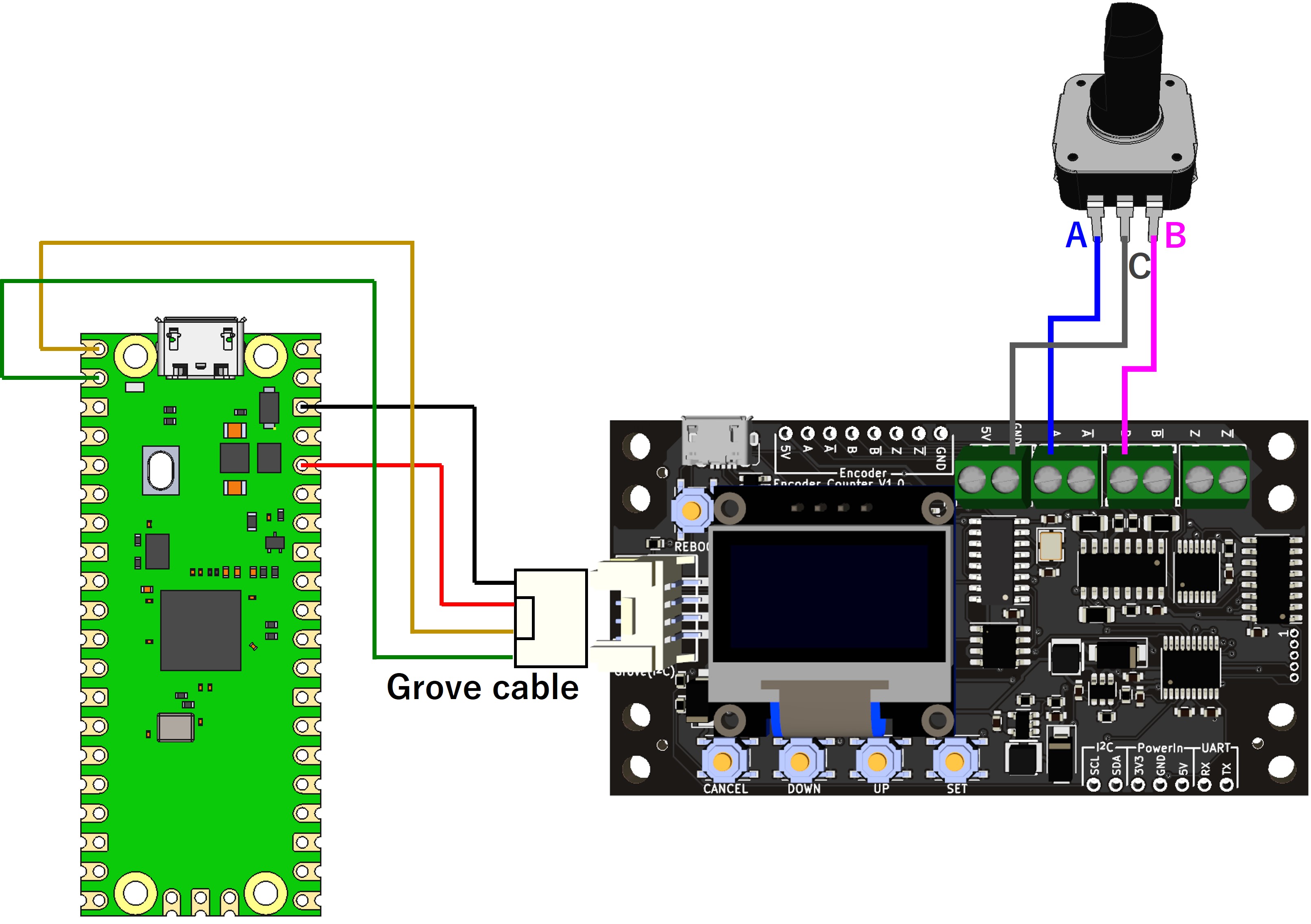
from machine import Pin, I2C
import utime
import struct
I2C_SLAVE_DEV_ADDR = 0x11
ECONF_REG_ADDR = 0x0B
CVAL_REG_ADDR = 0x03
# I2C init (SDA:0pin, SCL:1pin)
i2c = I2C(0, scl=Pin(1), sda=Pin(0), freq=100000)
# Write 0x07 to ECONF(0x0B)
i2c.writeto_mem(I2C_SLAVE_DEV_ADDR, ECONF_REG_ADDR, b'\x07')
# Wait until the config is written and the device reboots
print("Rebooting...")
utime.sleep(4)
while True:
utime.sleep(0.1)
# Read 4 bytes from CVAL(0x03)
data = i2c.readfrom_mem(I2C_SLAVE_DEV_ADDR, CVAL_REG_ADDR, 4)
# Little-endian conversion to type int32
value = struct.unpack('<i', data)[0] # '<' means little-endian
# Output result
print("val:", value)
USB接続で2台のエンコーダのカウント値を取得するプログラム例
配線図・サンプルコードを見る
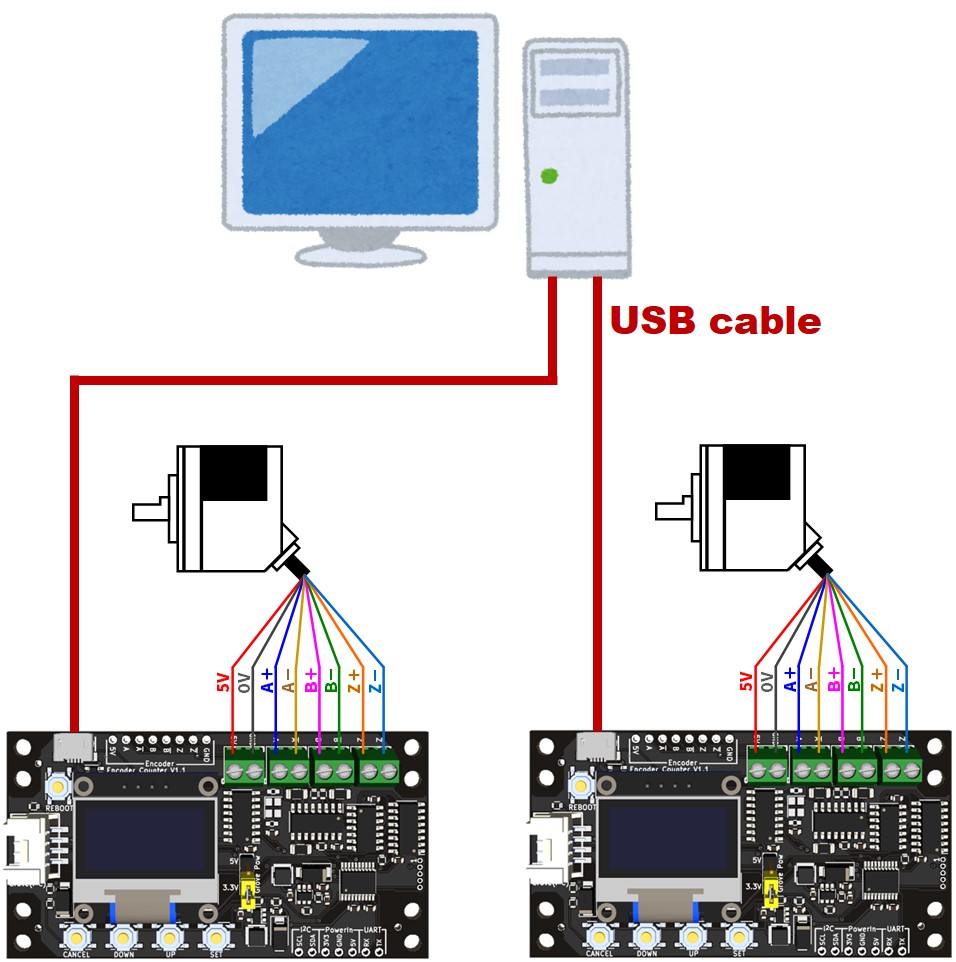
サンプルコード(.NET 6.0)
using System;
using System.IO.Ports; // https://www.nuget.org/packages/System.IO.Ports
using System.Collections.Concurrent;
public class Counter
{
public bool z_enable;
public int count, last_z_count;
public bool z_detected;
public Counter()
{
z_enable = false;
count = 0;
last_z_count = 0;
z_detected = false;
}
public void convertValue(string s)
{
string[] words = s.Split(':');
switch (words.Length)
{
case 1:
z_enable = false;
try
{
count = Int32.Parse(words[0]);
}
catch (FormatException)
{
Console.WriteLine($"Unable to parse '{s}'");
}
break;
case 3:
z_enable = true;
try
{
count = Int32.Parse(words[0]);
last_z_count = Int32.Parse(words[1]);
z_detected = Int32.Parse(words[2]) == 1 ? true : false;
}
catch (FormatException)
{
Console.WriteLine($"Unable to parse '{s}'");
}
break;
default:
Console.WriteLine($"Unable to parse '{s}'");
break;
}
}
}
public class Obtain2EncoderCounterValue
{
static bool _continue;
static SerialPort? _serialPort1, _serialPort2;
static ConcurrentQueue<Counter> _queue1 = new ConcurrentQueue<Counter>(), _queue2 = new ConcurrentQueue<Counter>();
public static void Main()
{
string message;
StringComparer stringComparer = StringComparer.OrdinalIgnoreCase;
Thread readThread1 = new Thread(Read1);
Thread readThread2 = new Thread(Read2);
Thread mergeThread = new Thread(Merge);
Console.WriteLine("Output synchronized values of 2 encoder counters\n");
printAvailablePorts();
Console.Write("First encoder counter: ");
_serialPort1 = new SerialPort(InputPortName(), 921600, Parity.None, 8, StopBits.One);
Console.Write("Second encoder counter: ");
_serialPort2 = new SerialPort(InputPortName(), 921600, Parity.None, 8, StopBits.One);
_serialPort1.ReadTimeout = 500;
_serialPort1.WriteTimeout = 500;
_serialPort2.ReadTimeout = 500;
_serialPort2.WriteTimeout = 500;
Console.WriteLine("{0}\t{1}", _serialPort1.IsOpen, _serialPort2.IsOpen);
_serialPort1.Open();
_serialPort2.Open();
_continue = true;
readThread1.Start();
readThread2.Start();
mergeThread.Start();
Console.WriteLine("Type QUIT to exit");
while (_continue)
{
message = Console.ReadLine()!;
if (stringComparer.Equals("quit", message))
{
_continue = false;
}
}
readThread1.Join();
readThread2.Join();
mergeThread.Join();
_serialPort1.Close();
_serialPort2.Close();
}
public static void Read1()
{
while (_continue)
{
try
{
Counter c = new Counter();
string message = _serialPort1!.ReadLine();
c.convertValue(message);
_queue1.Enqueue(c);
}
catch (TimeoutException) { }
}
}
public static void Read2()
{
while (_continue)
{
try
{
Counter c = new Counter();
string message = _serialPort2!.ReadLine();
c.convertValue(message);
_queue2.Enqueue(c);
}
catch (TimeoutException) { }
}
}
public static void Merge()
{
int i = 0;
while (_continue)
{
if(_queue1.Count() > 0 && _queue2.Count() > 0)
{
Counter c1, c2;
if(_queue1.TryDequeue(out Counter? a))
{
c1 = a!;
} else
{
continue;
}
if(_queue2.TryDequeue(out Counter? b))
{
c2 = b!;
} else
{
continue;
}
string text;
if(c1.z_enable && c2.z_enable)
text = $"{i++}\tc1:{c1.count},{c1.last_z_count},{c1.z_detected}\tc2:{c2.count},{c2.last_z_count},{c2.z_detected}";
else if(c1.z_enable && !c2.z_enable)
text = $"{i++}\tc1:{c1.count},{c1.last_z_count},{c1.z_detected}\tc2:{c2.count}";
else if(!c1.z_enable && c2.z_enable)
text = $"{i++}\tc1:{c1.count}\tc2:{c2.count},{c2.last_z_count},{c2.z_detected}";
else
text = $"{i++}\tc1:{c1.count}\tc2:{c2.count}";
Console.WriteLine(text);
File.AppendAllText(@"./output.txt", text.Replace(",", "\t").Replace("c1:", "").Replace("c2:", "") + '\n');
}
}
}
public static void printAvailablePorts()
{
Console.WriteLine("Available Ports:");
foreach (string s in SerialPort.GetPortNames())
{
Console.WriteLine("\t{0}", s);
}
}
public static string InputPortName()
{
string portName;
string[] ports = SerialPort.GetPortNames();
string defaultPortName = ports.Length >= 2 ? ports[^2] : "COM1";
Console.Write("Enter COM port value (Default: {0}): ", defaultPortName);
portName = Console.ReadLine()!;
if (portName == "" || !(portName.ToLower()).StartsWith("com"))
{
portName = defaultPortName;
}
return portName;
}
}
ダウンロード
- ソースコード
- 実行ファイル:Release.zip

